双向注意力LSTM神经网络
原理讲解
TextAttBiRNN是在双向LSTM文本分类模型的基础上改进的,主要是引入了注意力机制(Attention)。对于双向LSTM编码得到的表征向量,模型能够通过注意力机制,关注与决策最相关的信息。其中注意力机制最先在论文 Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate 中被提出,而此处对于注意力机制的实现参照了论文 Feed-Forward Networks with Attention Can Solve Some Long-Term Memory Problems。
注意力机制参考
请注意,这里的注意力机制与bert中transformer的注意力机制不同,transformer会更加复杂,大家可以参考我关于transformer
In the paper Feed-Forward Networks with Attention Can Solve Some Long-Term Memory Problems, the feed forward attention is simplified as follows,
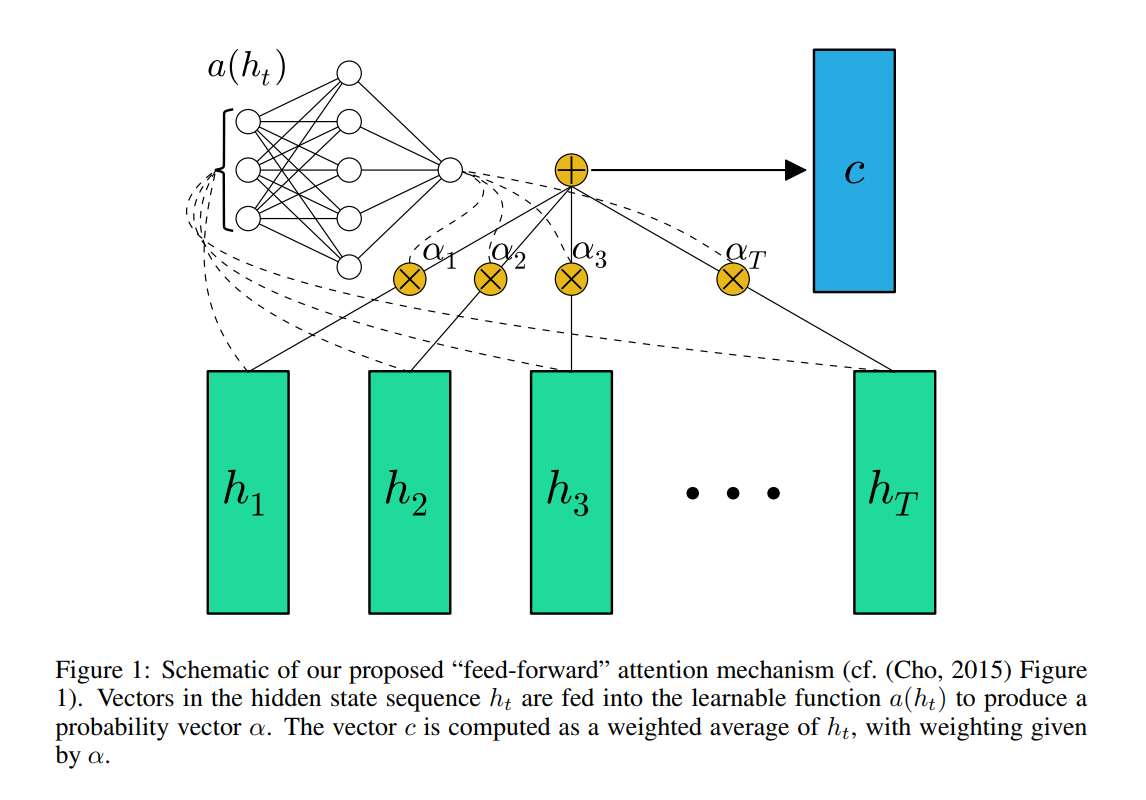
Function a, a learnable function, is recognized as a feed forward network. In this formulation, attention can be seen as producing a fixed-length embedding c of the input sequence by computing an adaptive weighted average of the state sequence h.
c就是注意力,alpha就是权重,h就是隐含状态,alpha通过softmax计算,score就是通过h计算的,h就是当前状态输入的词语和上一隐含状态ht-1计算而来的
细看结构
TextAttBiRNN 的网络结构
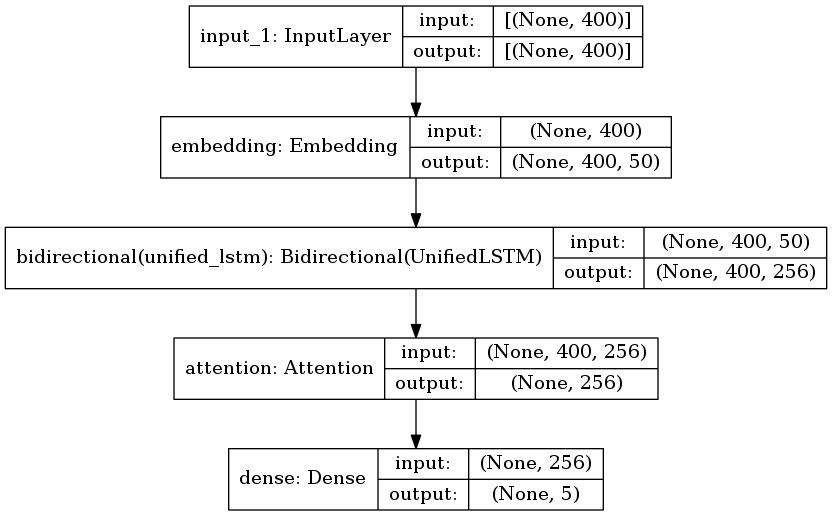
输入层
输入层我们可以定义为句子输入长度,每个词经过一个embedding_dim=50的embedding矩阵,最终输出400×50的表示矩阵.假设一个句子有400个词语
Bi-LSTM
Bi-LSTM层作为一种特征编码层,这层可以提取每个词语的上下文特征,然后将双向的特征进行拼接,然后依旧将每个词语的特征进行输出,因此输出为400×256的特征矩阵
Attention层 Attention层对这个网络中对每个词语进行了加权求和,这个权重是通过训练不断训练出来的,这层我们的输入x为400×256,我们初始化权重矩阵W为256×1维,然后对x与W进行点乘、归一化(公式的前两个),这样就可以得到400×1的矩阵a,这个矩阵代表的是每个词对应的权重,权重大的词代表注意力大的,这个词的贡献程度更大,最后对每个词语进行加权平均,aT与x进行点乘,得到1×256,这是最终加权平均后输出的总特征向量。
输出层 与我之前textCNN做中文新闻分类实验差不多,使用全连接层,softmax作为激活函数进行输出。
demo项目: 情感分析
导入工具包
import pandas as pd
import jieba_fast as jieba
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer
from tensorflow.keras import backend as K
from tensorflow.keras import initializers,regularizers,constraints
from tensorflow.keras import Input,Model,models
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding, Dense, Conv1D, GlobalMaxPooling1D, Concatenate, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras import Input,Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding,Dropout,Dense,Bidirectional,LSTM
from tensorflow.keras.models import load_model
from elmoformanylangs import Embedder
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
from pandarallel import pandarallel
pandarallel.initialize()
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
读取数据
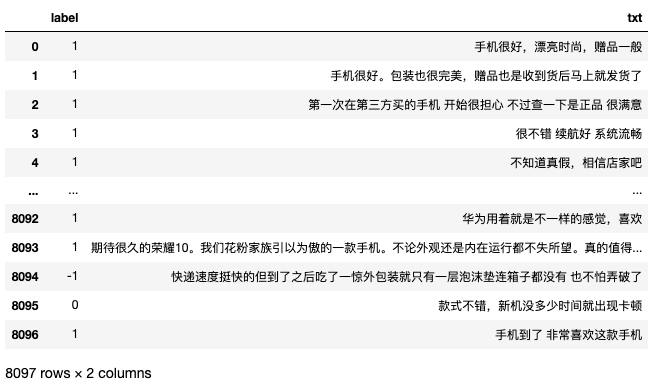
df = pd.read_csv('./data/sentiment_analysis_data.csv',sep=' ')
df
打乱样本
df = df.sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True)
建模思路
技术路线
分两种种情况,好评,负评,中评 计算路线: 1 使用TextCNN对每个句子类似n-gram处理
2 使用RNN
3 可以尝试使用attention机制做情感判断,对词进行word2vec,或者elmo embedding,可添加bi-lstm获取上下文信息
查看是否有缺失值
df.info()
分析标签数据情况
label_dict = {'-1':'负评','0':'中评','1':'正评'}
df['label']=df['label'].apply(lambda x: label_dict[str(x)] )
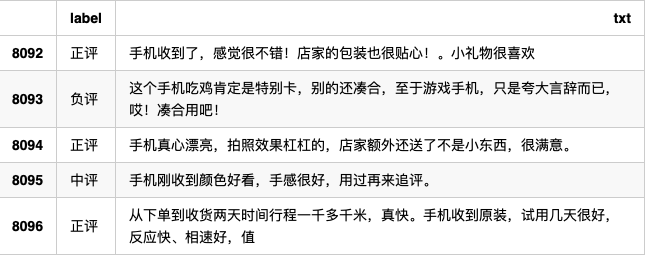
df.tail()
查看每个文本的长度
df['txt_num'] = df['txt'].agg(lambda x: len(x))
df.agg({'txt_num':'mean'})
得到句子长度
所以根据数据,得出我们会设置maxlen= 40左右
jieba分词
from pandarallel import pandarallel
pandarallel.initialize()
获取停用词和设立分词函数
stopwords = pd.read_csv('./data/stopwords.txt',sep='\t',index_col=False,quoting=3,encoding='utf-8')
def split_words(X):
result = [i for i in jieba.lcut(X) if i not in stopwords]
result = ' '.join(result)
return result
df['txt']=df['txt'].parallel_apply(split_words)
建立模型
Attention网络
class Attention(Layer):
def __init__(self, step_dim,
W_regularizer=None, b_regularizer=None,
W_constraint=None, b_constraint=None,
bias=True, **kwargs):
self.supports_masking = True
self.init = initializers.get('glorot_uniform')
self.W_regularizer = regularizers.get(W_regularizer)
self.b_regularizer = regularizers.get(b_regularizer)
self.W_constraint = constraints.get(W_constraint)
self.b_constraint = constraints.get(b_constraint)
self.bias = bias
self.step_dim = step_dim
self.features_dim = 0
super(Attention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def build(self, input_shape):
assert len(input_shape) == 3
self.W = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[-1],),
initializer=self.init,
name='{}_W'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.W_regularizer,
constraint=self.W_constraint)
self.features_dim = input_shape[-1]
if self.bias:
self.b = self.add_weight(shape=(input_shape[1],),
initializer='zero',
name='{}_b'.format(self.name),
regularizer=self.b_regularizer,
constraint=self.b_constraint)
else:
self.b = None
self.built = True
def compute_mask(self,input,input_mask=None):
#do not pass the mask to the next layers
return None
def call(self,x,mask=None):
features_dim = self.features_dim
step_dim = self.step_dim
#K.reshape(x,(-1,features_dim))里面-1可以想象成一行,features_dim变成一行有features_dim维矩阵(1*dim维),K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1)),变成矩阵(dim维*self.W)features_dim行和1维
e = K.reshape(K.dot(K.reshape(x, (-1, features_dim)), K.reshape(self.W, (features_dim, 1))), (-1, step_dim))
# 这里也可以用另外一种表示方式
# e = K.reshape(K.dot(K.reshape(x,(1,-1)),K.reshape(self.W,(-1,1))),(-1,1))
# 其实就是全连接的矩阵相乘 e = K.dot(x, self.W)
if self.bias:
e += self.b
e = K.tanh(e) # 激活函数
a = K.exp(e) # 去指数
# apply mask after the exp. will be re-normalized next
if mask is not None:
# cast the mask to floatX to avoid float64 upcasting in theano
a *= K.cast(mask, K.floatx()) # 转换成floatx类型
# in some cases especially in the early stages of training the sum may be almost zero
# and this results in NaN's. A workaround is to add a very small positive number ε to the sum.
a /= K.cast(K.sum(a, axis=1, keepdims=True) + K.epsilon(), K.floatx()) # softmax函数,得到权重矩阵
a = K.expand_dims(a) # 变成(dim,1),这样可以与x进行加权就和得到context
c = K.sum(a*x,axis=1) #权重与hidden信息加权就和得到context,也就是我们的注意力
return c
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape[0], self.features_dim
def get_config(self):
config = {
"step_dim":self.step_dim,
"W_regularizer":self.W_regularizer, "b_regularizer":self.b_regularizer,
"W_constraint":self.W_constraint, "b_constraint":self.b_constraint,
"bias":self.bias}
base_config = super(Attention, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
网络结构
elmo层
哈工大开发的动态词向量elmo
elmo原理可参考链接
e = Embedder('./zhs.model/')
创建padding函数
超过句子长度就截取,不够就补空
def pad_sent(x, max_len):
if len(x)>max_len:
return x[:max_len]
else:
return x+['']*(max_len-len(x))
创建批量生成器
def batch_generator(x, y, batch_size=64):
n_batches_per_epoch = len(x)//batch_size
for i in range(n_batches_per_epoch):
x_batch = np.array(e.sents2elmo([pad_sent(sent,40) for sent in x[batch_size*i:batch_size*(i+1)]]))
y_batch = y[batch_size*i:batch_size*(i+1),:]
yield x_batch, np.array(y_batch)
def predict_generator(x, batch_size=1): #预测
n_batches_per_epoch = len(x)//batch_size
for i in range(n_batches_per_epoch):
x_batch = np.array(e.sents2elmo([pad_sent(sent,40) for sent in x[batch_size*i:batch_size*(i+1)]]))
yield x_batch
构建ELMOTextBiRNN网络结构
class ELMOTextBiRNN(object):
def __init__(self,maxlen,max_features,embedding_dims,class_num=3,last_activation='softmax'):
self.maxlen = maxlen
self.max_features = max_features
self.embedding_dims = embedding_dims
self.class_num = class_num
self.last_activation = last_activation
# def get_model(self):
# embedding = Input((self.maxlen, self.embedding_dims,)) # 输入预训练的词向量
# convs = []
# for kernel_size in [3,4,5]: #设定filter大小
# c = Conv1D(128,kernel_size,activation='relu')(embedding)
# c = GlobalMaxPooling1D()(c)
# convs.append(c)
# x = Concatenate()(convs)
# output = Dense(self.class_num,activation=self.last_activation)(x)
# model = Model(inputs=embedding,outputs=output)
# return model
def get_model(self):
embedding = Input((self.maxlen,self.embedding_dims,))
x = Bidirectional(LSTM(128,return_sequences=True))(embedding)
x = Attention((self.maxlen))(x)
output = Dense(self.class_num,activation=self.last_activation)(x)
model = Model(embedding,output)
return model
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(df['txt'].values)
vocab = tokenizer.word_index
len(vocab)+1
设置模型参数
maxlen = 40
batch_size = 32
max_features = len(vocab)+1
embedding_dims = 1024
epochs = 9
获取模型
model = ELMOTextBiRNN(maxlen,max_features,embedding_dims).get_model()
plot_model(model,show_shapes=True)
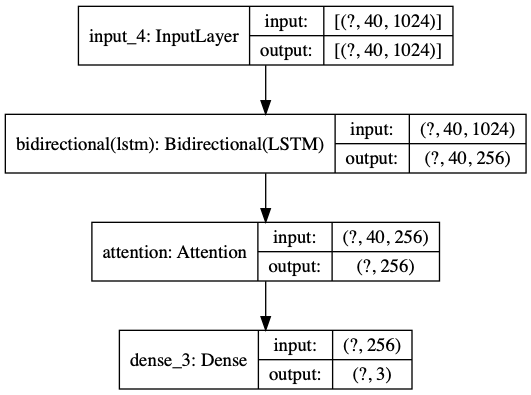
划分训练集,测试集
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(df['txt'].values,df['label'])
建立词典,词语id化,标签独热编码
def encode_category_one_hot(y_train,y_test):
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
set(y_train)
categories = set(y_train)
categories
cat_to_id = dict(zip(categories, range(len(categories))))
y_train_id = [cat_to_id[i] for i in y_train]
y_test_id = [cat_to_id[i] for i in y_test]
cat_to_id
y_train_one_hot = to_categorical(y_train_id)
y_test_one_hot = to_categorical(y_test_id)
return y_train_one_hot,y_test_one_hot,cat_to_id
y_train_one_hot,y_test_one_hot,cat_to_id = encode_category_one_hot(y_train,y_test)
x_train = sentences_list(x_train)
x_test = sentences_list(x_test)
设立早停
my_callbacks = [ModelCheckpoint('.ELMO_birnn_model.h5'),
EarlyStopping(monitor='accuracy',patience=2,mode='max')]
model = ELMOTextBiRNN(40,max_features,1024).get_model()
model.compile('adam','categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
测试模型
text = '今天 天气 很 晴朗 处处 有 阳光 有 阳光'
sentence = [['%s'%text]]
cat_to_id
{'负评': 0, '正评': 1, '中评': 2}
sentence
[['今天 天气 很 晴朗 处处 有 阳光 有 阳光']]
model.predict_generator(predict_generator(sentence, batch_size=1),steps=1)
array([[0.21561107, 0.600974 , 0.18341494]], dtype=float32)